China set for first Stirling CSP plant; Morocco shortlists five bidders for giant PV-CSP tender
Our pick of the latest solar thermal news you need to know.

Related Articles
Cleanergy, Datang agree to develop China's first Stirling CSP plants
Sweden's Cleanergy and China's Datang Holdings New Energy Technologies are planning to build 200 MW of Stirling CSP capacity after the firms executed a technology agreement set out earlier this year, Cleanergy said in a statement June 14.
In April, Cleanergy and Datang agreed to jointly manufacture, develop and install Cleanergy's Stirling CSP technology. Datang has now paid Cleanergy a commitment fee of RMB 5 million (SEK 6.4 million) and the partners will now go ahead with the construction of a 50 MW CSP plants by 2018 followed by a 150 MW plant including energy storage, Cleanergy said.
Under the plan, Cleanergy would become the first CSP developer to install large-scale Stirling technology in China. China currently plans to build 1.3 GW of CSP capacity by 2018 in a first batch of 20 CSP projects which includes nine solar towers, seven parabolic trough plants and four Linear Fresnel plants. China is expected to follow the first deployment round with another wave of projects.
The 200 MW Cleanergy-Datang project has a potential value of around SEK 5 billion and Cleanergy would supply around half of this value, it said. Datang will secure Chinese government approvals and other financing.
Cleanergy and Datang are currently studying the full cost reduction potential of localizing production in China, starting with component sourcing and assembly of the dish concentrator, Cleanergy said.
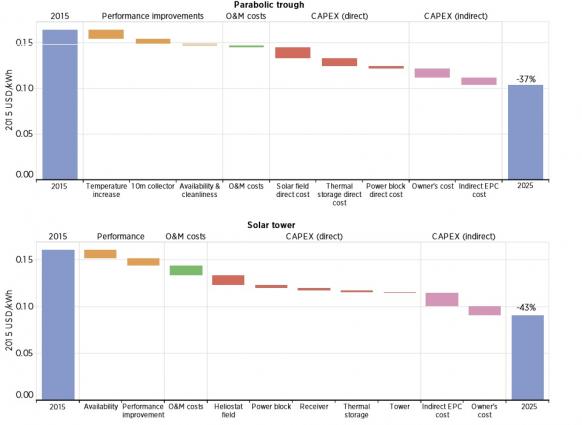
Global CSP LCOE reduction potential by 2025
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), DLR (2016).
Morocco shortlists five international bids for Noor Midelt PV-CSP project
Five CSP consortia have prequalified to bid for Morocco's Noor Midelt Phase I combined PV and CSP project, the Moroccan Agency for Solar Energy (MASEN) said in a statement. Noor Midelt Phase I consists of two hybrid PV-CSP projects each of CSP gross capacity 150 MW-190 MW.
The five shortlisted consortia are led by Saudi Arabia's ACWA Power, France's EDF EN, Engie (formerly GDF Suez), Germany's Innogy and Japan's JGC. Seven consortiums submitted applications to prequalify for the tender in November 2016.
The Noor Midelt project is to be developed through an independent power producer (IPP) scheme in which the successful consortium designs, finances, builds and operates the plants.
Under the tender requirements, the CSP technology must be a synthetic oil parabolic trough system with storage or a molten salt tower with storage, official documents show.
The Moroccan government has chosen to support hybrid PV-CSP plants for Noor Midelt to provide low-cost power output during the day and electricity supply after sunset.
While PV with batteries are seen as the most economic solar solution for storage durations of a few hours, CSP plants offer lower generation costs across longer storage periods.
Morocco has set a target of installing 10 GW of wind and solar power by 2030 and the country has been a frontrunner in CSP deployment.
The government has preselected solar development sites at Ouarzazate and Midelt, both situated in central Morocco.
Noor Ouarzazate, the first solar complex, will host three CSP plants of combined capacity 510 MW as well as 70 MW of PV capacity. All three CSP plants have storage capacity.
The first project, Noor I, a 160 MW CSP parabolic trough plant, is already operational. The 200 MW Noor II parabolic trough plant and 150 MW Noor III tower plant have both reached financial closure and are under construction.
A fourth phase at Ouarzazate, Noor IV, will see two PV plants developed with a combined capacity of 70 MW.
New Energy Update