China PV limit to slice module prices by a third; US installs 2.5 GW of solar in Q1
Our pick of the latest solar news you need to know.

Related Articles
China installation quota to cut 2018 module prices by a third
Chinese PV module prices could fall by around 35% in 2018 following new national limits on installations, according to analysts at Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF).
The Chinese government's 2018 Solar PV Generation Notice-- issued on May 31-- sets hard limits on PV installations in China this year. The move creates a module supply surplus that will impact global prices.
Following the announcement, IHS Markit lowered its outlook for global PV installations in 2018 from 113 GW to 105 GW, still 11% higher than in 2017.
"This sudden slump in China will reshape the whole PV supply chain. Supply-chain producers with a significant share of business in China will be placed under great pressure, causing a fiercely competitive environment in international markets, which will lead to aggressive price reductions across the board," IHS Markit said in a note.
A global price war on solar modules will "reignite PV demand in regions with pent-up demand, where buyers have kept projects on hold while waiting for lower module prices," it said.
The impact on global module prices will depend somewhat on Europe's minimum import price (MIP) rules, on which the European Commission (EC) faces a decision in August. Prices could also depend on India's decision on anti-dumping and safeguard duties.
"In the U.S. market, lower international prices will counteract the 201 case import duties and increase module imports," IHS Markit said.
"The precise outcome, in terms of [global] volumes installed, will depend on the appetite of quickly emerging regions to procure modules in the second half of the year or bet on additional price declines. For now, many projects and orders are on hold, with developers and engineering procurement construction firms (EPCs) fully aware that the industry flipped to a buyers’ market overnight," it said.
U.S. installs 2.5 GW of PV capacity in Q1 as import tariffs clip growth
The U.S. installed 2.5 GW of PV capacity in the first quarter of 2018, up by 13% on a year ago but down 37% quarter on quarter, GTM Research said in its latest quarterly market report. Utility-scale projects represented 1.4 GW of new installations, the research group said.
"In Q1 2018, 50% of all new electric generating capacity brought online in the U.S. came from solar-the second consecutive quarter in which solar accounted for the largest share of new capacity additions," it said.
GTM Research predicts 10.8 GW of solar power will be installed in 2018, a similar level to 2017. Some 6.6 GW of this will be utility-scale and this takes into account new import tariffs on cells and modules.
"While securing some tariff-free modules has provided relative insulation from 2018 projects, developers are still facing the prospect of higher module costs over the long term," it said.
Delays to projects and requests for proposals (RfPs) following the import tariffs have prompted GTM Research to lower its 2019 utility-scale forecast by 600 MW to 7.0 GW.
"For existing projects that did not factor in tariffs, several developers have reported that they are still trying to renegotiate PPA [power purchase agreement] prices with the utility offtaker. Consequently, we expect to hear of project cancellations in H2 2018," it said.
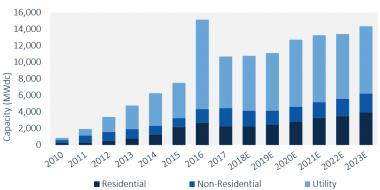
US PV installation forecast by segment
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: GTM Research, June 2018.
GTM Research predicts U.S. utility-scale installations will rise to 8.1 GW per year in 2020 and 2021.
"As procurement picks up for new projects, both developers and offtakers are targeting 2020 and 2021 completion dates so that projects are able to secure the 30% ITC [investment tax credit] in 2019 using the law’s commence-construction provision, but can still purchase modules at a lower tariff rate in 2020 or 2021," it said.
Investor-owned utilities (IOUs) such as Duke Energy in North Carolina and Florida Power & Light have outlined consistent annual procurement targets and this will drive the bulk of capacity additions during this time, GTM Research said.
Corporate procurement of utility-scale PV now represents 10% of projects in development and these groups will continue to drive new project development through 2022 as they try to acquire PPAs before the ITC steps down, it noted.
US utility-scale solar pipeline
(Click image to enlarge)
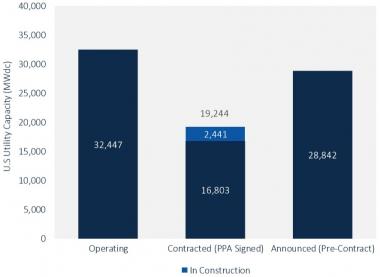
Source: GTM Research, June 2018.
Tech groups join forces to improve renewables PPA regulation
Leading global technology companies have become steering group members of Europe's RE-Source Platform, which pools resources to accelerate regulatory changes to accommodate corporate wind and solar energy contracts.
Google, Microsoft, IKEA Group, BT, Danone, Amazon, Enel Green Power, Engie, RES, Novartis, Iberdrola and Facebook, Inc, have all joined the scheme, industry groups WindEurope and SolarPower Europe announced June 6.
The RE-Source Platform aims to accelerate wind and solar investments by improving regulatory frameworks for corporate renewable power purchase agreements (PPAs). In some European countries, regulatory barriers have hampered PPA negotiations.
Technology groups have led a recent surge in renewable PPA activity. Over 1 GW of renewable PPA deals were signed in Europe in 2017 and the potential for more is "huge," WindEurope and SolarPower Europe said. In comparison, U.S. wind developers signed 3.6 GW of power purchase agreements (PPAs) in the first quarter of 2018 alone, the highest level recorded to date, the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) said May 4.
“As the world’s largest corporate buyer of renewable energy, we are excited to support the RE-Source platform to accelerate the growth of renewables in Europe,” Marc Oman, Senior Lead, Energy and Infrastructure, Google, said in a statement.
"We look forward to being part of the RE-Source Platform, which brings together a multitude of stakeholders and voices committed to advancing regulatory frameworks that enable more corporate investments in renewable energy, taking us ahead in our journey towards a greener Europe,” Adina Braha-Honciuc, Government Affairs Manager at Microsoft, said.
New Energy Update