Global solar installs forecast to rise 6% in 2018; Solar plus storage represents 40% of storage pipeline
Our pick of the latest solar news you need to know.

Related Articles
Global solar growth forecast at 6% in 2018 but top markets slide
Annual installations of solar capacity are expected to rise by 6% to 104 GW in 2018, according to the latest Global Solar Demand Monitor published by GTM Research. Annual installations will remain above 100 GW through at least 2022, the report said.
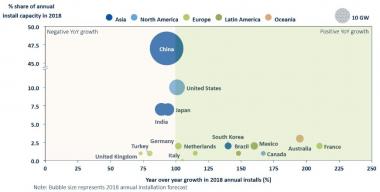
While total installations are expected to rise this year, installations in the top four markets of China, U.S., Japan and India are expected to collectively fall by 7%.
Installations in China, the largest market, will drop from 53 GW in 2017 to 48 GW in 2018, GTM Research said.
Global solar growth forecast for 2018
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: GTM Research (April 2018).
Solar plus storage accounts for 40% of energy storage pipeline
Solar plus storage projects currently represent more than 40% of the global pipeline for grid-scale energy storage, IHS Markit said in a report published April 16.
Annual grid-connected battery energy storage installations grew by 53% in 2017 to 1.9 GW, the highest level on record. More than 3 GW of battery energy storage is forecast to be deployed in 2018 and the global project pipeline for storage projects grew to 10.4 GW at the end of the first quarter of 2018, IHS Markit said.
"The global battery energy storage market gained significant momentum in early 2018. Emerging business models, such as gas-peaker replacement and renewable firming, have been successfully demonstrated, leading to a strong uptick in the global pipeline," it said.
The geographic location of planned project activity is diversifying and the largest current pipelines are located in Australia, UK, U.S. and China. IHS Markit predicts the behind-the-meter storage segment will comprise more than half of annual storage installations from 2023.
In the U.S., new energy storage deployment targets, and the inclusion of storage in integrated resource planning will drive future market growth across multiple states, the research group said.
Supportive U.S. policy developments include FERC Order No. 841, which will remove key regulatory barriers for electricity storage to participate in wholesale markets, and New York State's target to deploy 1,500 MW by 2025, supported by more than $260 million of funding.
IHS Markit also said that battery energy storage is challenging the competitiveness of gas-fired peaker plants in California, "leading to a significant increase in the outlook for large-scale energy storage in that state."
In Europe, Irish grid operator EirGrid has published its consultation on the DS3 program, which outlines proposed six-year contracts for frequency response and reserve services to be launched in September 2018. Austria has also launched a federal subsidy program for small-scale solar plus storage while several states in Germany have announced new support programs for residential storage, IHS noted.
US to provide $106 million to solar operations, manufacturing research
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is to provide up to $105.5 million to around 70 solar research projects across the PV and CSP sectors, the DOE announced April 17.
The funding program includes $46 million towards projects which advance solar power electronics, solar plus storage, PV-integrated sensor technologies and grid resilience.
By April 18, the DOE had allocated $20 million to nine PV power electronics projects.
Advances in power electronics can help grid operators rapidly detect and respond to problems, protect against physical and cyber vulnerabilities, and enable consumers to manage electricity use, the DOE noted.
“There is remarkable potential for power electronics technologies to improve the reliability and flexibility of solar energy on the grid,” Daniel Simmons, Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, said.
The DOE will also allocate $27 million to research projects which increase PV module performance, reduce materials and processing costs and improve reliability of cells, modules and systems, it said.
"These projects support DOE’s efforts to lower LCOE to $0.03 per kilowatt hour [$30/MWh) from utility-scale systems by 2030," the department said.
A further $8.5 million will be provided for workforce initiatives that "prepare the solar industry for a digital future while also increasing the number of veterans and participants in the solar industry," it said.
The DOE will also provide $24 million to Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) research.
New Energy Update